Location Area (LA)
A GSM network is divided into cells. A group of cells is considered a location area. A mobile phone in motion keeps the network informed about changes in the location area. If the mobile moves from a cell in one location area to a cell in another location area, the mobile phone should perform a location area update to inform the network about the exact location of the mobile phone.
The Location Update procedure is performed:
- When the MS has been switched off and wants to become active, or
- When it is active but not involved in a call, and it moves from one location area to another, or
- After a regular time interval.
Location registration takes place when a mobile station is turned on. This is also known as IMSI Attach because as soon as the mobile station is switched on it informs the Visitor Location Register (VLR) that it is now back in service and is able to receive calls. As a result of a successful registration, the network sends the mobile station two numbers that are stored in the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card of the mobile station.
These two numbers are :-
- Location Area Identity (LAI)
- Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI).
- A Location Area Identity (LAI) is a globally unique number.
- A Location Area Code (LAC) is only unique in a particular network.
A channel request message is sent that contains the subscriber identity (i.e. IMSI/TMSI) and the LAI stored in the SIM card. When the target MSC/VLR receives the request, it reads the old LAI which identifies
the MSC/VLR that has served the mobile phone up to this point. A signalling connection is established between the two MSC/VLRs and the subscriber’s IMSI is transferred from the old MSC to the new MSC. Using this IMSI, the new MSC requests the subscriber data from the HLR and then updates the VLR and HLR after successful authentication.
Periodic location update is carried out when the network does not receive any location update request from the mobile in a specified time. Such a situation is created when a mobile is switched on but no traffic is carried, in which case the mobile is only reading and measuring the information sent by the network. If the subscriber is moving within a single location area, there is no need to send a location update request.
A timer controls the periodic updates and the operator of the VLR sets the timer value. The network broadcasts this timer value so that a mobile station knows the periodic location update timer values.
Therefore, when the set time is up, the mobile station initiates a registration process by sending a location update request signal. The VLR receives the request and confirms the registration of the mobile in
the same location area. If the mobile station does not follow this procedure, it could be that the batteries of the mobile are exhausted or the subscriber is in an area where there is no network coverage. In such
a case, the VLR changes the location data of the mobile station to “unknown”.
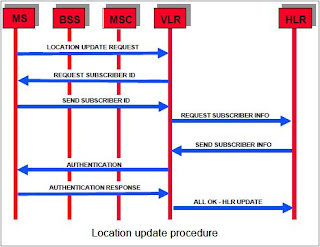
The Location Update process consists of the following phases
- Request for service; the MS detects that it has entered a new Location Area and requests to update its location. The new MSC/VLR identifies the MS.
- Authentication - The new MSC/VLR requests to the AUC for authentication parameters (SRES, Kc, RAND). Using these parameters the MS is authenticated.
- Ciphering - Using the parameters which were made available earlier during the authentication the uplink and the downlink are ciphered.
- Update HLR/VLR - The new MSC/VLR requests to update the MS location in the HLR. The MS is de-registered in the old VLR.
- TMSI re-allocation - The MS is assigned a new TMSI.
- The MS detects that it has entered a new Location Area and transmits a Channel Request message over the Random Access Channel (RACH).
- Once the BSS receives the Channel Request message, it allocates a Stand-alone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) and forwards this channel assignment information to the MS over the Access Grant Channel (AGCH). It is over the SDCCH that the MS will communicate with the BSS and MSC.
- The MS transmits a location update request message to the BSS over the SDCCH. Included in this message are the MS Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI) and the old Location Area Identification (oldLAI). The MS can identify itself either with its IMSI or TMSI. The BSS forwards the location update request message to the MSC.
- The VLR analyzes the LAI supplied in the message and determines that the TMSI received is associated with a different VLR (old VLR). In order to proceed with the registration, the IMSI of the MS must be determined. The new VLR derives the identity of the old VLR by using the received LAI, supplied in the location update request message. It also requests the old VLR to supply the IMSI for a particular TMSI.
- The new VLR sends a request to the HLR/AUC (Authentication Center) requesting the “authentication triplets” (RAND, SRES, and Kc) available for the specified IMSI.
- The AUC, using the IMSI, extracts the subscriber's authentication key (Ki). The AUC then generates a random number (RAND), applies the Ki and RAND to both the authentication algorithm (A3) and the cipher key generation algorithm (A8) to produce an authentication Signed Response (SRES) and a Cipher Key (Kc). The AUC then returns to the new VLR an authentication triplet: RAND, SRES, and Kc.
- The MSC/VLR keeps the two parameters Kc and SRES for later use and then sends a message to the MS. The MS reads its Authentication key (Ki) from the SIM, applies the received random number (RAND) and Ki to both its Authentication Algorithm (A3) and Cipher key generation Algorithm (A8) to produce an authentication Signed Response (SRES) and Cipher Key (Kc). The MS saves Kc for later, and will use Kc when it receives command to cipher the channel.
- The MS returns the generated SRES to the MSC/VLR. The VLR compares the SRES returned from the MS with the expected SRES received earlier from the AUC. If equal, the mobile passes authentication. If unequal, all signaling activities will be aborted.
- The new MSC/VLR requests the BSS to cipher the radio channel. Included in this message is the Cipher Key (Kc), which was made available earlier during the authentication.
- The BSS retrieves the cipher key, Kc, from the message and then transmits a request to the MS requesting it to begin ciphering the uplink channel.
- The MS uses the cipher key generated previously when it was authenticated to cipher the uplink channel, and transmits a confirmation over the ciphered channel to the BSS.
- The BSS upon ciphering the downlink channel sends a cipher complete message to the MSC. At this point, we are ready to inform the HLR that the MS is under control of a new VLR and that the MS can be de-registered from the old VLR.
- The new VLR sends a message to the HLR informing it that the given IMSI has changed locations and can be reached by routing all incoming calls to the VLR address included in the message.
- The HLR requests the old VLR to remove the subscriber record associated with the given IMSI. The request is acknowledged.
- The HLR updates the new VLR with subscriber data (mobiles subscriber’s customer profile).
- The MSC forwards the location update accept message to the MS. This message includes the new TMSI.
- The MS retrieves the new TMSI value from the message and updates its SIM with this new value. The mobile sends then an update complete message back to the MSC.
- The MSC requests from the BSS that the signaling connection be released between the MSC and the MS.
- The MSC releases its portion of the signaling connection when it receives the clear complete message from the BSS.
- The BSS sends a "radio resource" channel release message to the MS and then frees up the Stand-alone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) that was allocated previously. The BSS then informs the MSC that the signaling connections has been cleared.
More Information from Readers are Expected !!!
Thanks
telecomtigers@gmail.com
http://homepageforu.webs.com/













Perfect and all the process are clearly mentioned....tnx mate :) Expect more informations regarding security issues of GSM and 3G from u tigers....Gud luck.
ReplyDeleteIt is written: "The MS reads its Authentication key (Ki) from the SIM".
ReplyDeleteIn reality the Ki shall never leave the SIM and is thus not "read from the SIM". The cryptographic algorithm is executed internally on the SIM and only the result returned to the phone.
@Anonymous: Thanks for correcting us... you are absolutely correct....Ki never leaves SIM.
ReplyDeleteWhat if the mobile is in idle mode?
ReplyDeleteHow can we identify a mobile station in idle mode?
If the mobile communicates with the BTS frequently during idle mode, what will be the minimum time period?
Please send me a reply for these questions to josefmathew004@gmail.com
Thanks & Regards:- Joseph Mathew
Dear Josef,
ReplyDeleteSorry for late response ....
Answers to all your question revolves around term "Periodic Location Update".
Periodic location update is procedure through which MSC comes to know whether mobile is active or not.
What if the mobile is in idle mode?
In idle mode there is Periodic Location update timers that keeps ticking in Mobile station.
This timer is BTS specific and can be set according to network requirement and planning. Timer value is set and BTS and broad casted to all mobile stations under coverage of BTS.
On expiry of this timer Mobile station has to do mandatory Locupd this Locupd is called Periodic Location update.
One can see "type of location update" bit in trace.
0--> Signifies Normal Location Update
1--> Periodic Location update
How can we identify a mobile station in idle mode?
In idle mode MS only keeps listening to PGCH channel to responds in case it finds his own IMSI or TMSI
If the mobile communicates with the BTS frequently during idle mode, what will be the minimum time period?
Minimum time period for communication with BTS in idle mode will be "periodic location update timer".
Feel free to revert for further Queries...........
ChEEEErS!!!!
Telecom TigerS
can you please explain me the procedure of update location during a call?? will there be any update in the hlr or the call will be forwarded from vlr-1 to vlr-2?? ( vlr-1 : previous vlr where the call was initiated & vlr-2 : present vlr)
ReplyDeleteDear Anonymous,
ReplyDeleteThere is no information shared with HLR during call when subscriber moves form one VLR to another VLR.
Normal location update will initiate as soon as call is ended in VLR2 and new VLR will be updated in HLR after that.
Thanks for your quick reply. can you please tell me the use of FACCH in the radio channel. I heard that FACCH will take care of fast handoff during call by replacing speech data with signaling data. so if no location update happens during a call then what is the use of FACCH??
ReplyDeleteDear,
ReplyDeleteFACCH is not designed to carry location related messages like "location update request", "Authentication request" etc.
It can only carry "Handover" and "Power" related Messages like "Imsi detach" & "Ho performed" etc during the call.
Thanks for ur answer. i want to ask you one more question. if there is no UL happening during a call, the hlr will not be updated about the new vlr right?? so the first vlr where the call was initiated will remember the address of the new vlr and diverts the signaling to it for maintaining the session and to send SMS etc., right??
ReplyDeleteDear,
ReplyDeleteSorry for late response...
you are correct HLR will not be updated in handover case.
Old VLR wont divert any signaling to new VLR.
Regarding SMS they will be only delivered after fresh UL in new VLR.
During the Periodic Location Update any signaling traffic is initiated towards the HLR or not..?
ReplyDeleteAnd also what is the advantage of using the IMEISV (IMEI Software Version) during the periodic location update.
Hi Rahul,
ReplyDeleteIn Location Update, signaling traffic will only be intited towards HLR in case of VLR change & fresh Location Update.
IMEI & IMEISV is mainly used for mobile handset security.
Feel free to revert for further Queries...........
Thanks
Gaurav Goel
Hi, I have a question.
ReplyDelete1)Is LAC stored in SIM card or the handset?
2)Is LAC sent to network during every location update procedure?
if one person is moving from one msc to other msc during call conversation then what about Location update and hand over.
ReplyDelete@priyaranjan:handover and LU take place when any mobile is in idle mode...no interMSC HO and LU take place when any MS is in busy condition..
ReplyDeleteAshok: Will Authentication happen for the Periodic LU also?
ReplyDeleteAshok : Can you please explain about 3G Authentication..
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteI want to know does a new TMSI is assigned in periodic location update or not?
Hi,
ReplyDeleteI want to know the average time duration for the complete procedure of Location area update.
@Tini: No TMSI is not allocated in case of periodic location update
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteThere is no such standard for average time duration for location update.
According to current scenario wherein Authentication,EIR check and Chipering is compulsary , location update should ideally complete in less than 4-5 sec.
What should happen first EIR check or Ciphering any recommendations on the sequence of events?
DeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteCan i know what error messages can we expect in update location response.
@Gaurav
ReplyDelete"no inter MSC HO takes place, when MS is in busy state"
. could you please explain.
Is it mean no HO for inter MSC when MS is in conversation
@gaurav can u explain then what happens to the call when it moves from one location to other (i.e)from one MSC to other MSC but in conversation ??
Delete@venkat :during call conversation inter msc HO takes place.after call disconnected LU initated by new msc.and during conversation mobile is always attached by old msc.
ReplyDelete@priyaranjan, LU is initiated by the MS or UE not by the MSS/VLR.
DeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteI have a question about the "periodic Location update",
is it the same procedure as in the sketch for normal "Location update"? I dont think so because, there is no new VLR?What is the procedure in this case?
I hope you can unterstand,
with best regards
Peter
@priyaranjan,
ReplyDeleteNew LU is initiated by the MS or UE not by the MSS/VLR.
Hi,
ReplyDeleteIn the periodic LU procedure it is mentioned that "In such
a case, the VLR changes the location data of the mobile station to “unknown”."
But MSS/VLR sets the MS/UE as absent and MNRF flag is set in the HLR.
So that for any further incoming calls or SMS, MS/UE won't be paged. By this way radio resources can be saved from paging.
@Anonymous & @Tini
ReplyDeleteTMSI can be allocated by MSS/VLR during a periodic location update and it can be set by the operator (i.e. to be allocated or not).
@T.S.Ashok,
Yes authentication can happen to periodic location update too and it can be set by the operator (i.e. to be done or not)
@Anonymous :Aside from fresh location update, an implicit detach timer is introduced in the VLR for the IMSI status management. In addition, measures are taken in BSS to force the MS to report its location periodically.Therefore, the network is informed of the status of MS. The network sends a periodic location updating time T3212 to all the users in the cell through BCCH to force the MS to send location updating request with the cause of periodic location updating after T3212 times out.After receiving Location update Request From MS.
ReplyDeleteMSC has subscriber data in vlr(Set of triplet,subscriber basic info etc) so this requset not send to HLR.MSC send RAND(same triplet used which one received in fresh location update for perticuler MS from HLR) to MS.MS reply back with SRES.MSC compairs SRES->if matched location update acceptd.
@ Anonymous
ReplyDeletei knew one error msg "illegle MS" if SRES not matched .
what happens to MS when Periodic LU timer in a BTS is changed to anew value? Do all the MS in the coverage go for simultaneous LU or is the timer in MS reset and starts calculating for the new timer?
ReplyDeleteHi,how is location area update procedure different from routing area update procedure?
ReplyDeleteAny difference when a prepaid subscriber is doing location update
ReplyDelete